Knowledge construction is the step-wise
process of learning through which we build upon pre-existing experiences and
prior understanding. It is based on the premise that our current knowledge
influences not only what we learn, but the way in which we learn. Although learners
have different styles and preferences, knowledge construction is thought to be
a common process for all learners.
Knowledge construction begins by connecting. During this step, learners
are provided with resources such as textbooks and validated online references,
and are prompted to complete assignments to build upon existing knowledge. The
next step, communicating, is achieved
by the sharing or elaborating on the material. This may be achieved through any
type of informational presentation, such as student-led presentations, topic
discussions, and group assignments. Next, collaborating
is achieved when teachers and learners review the assignments, contrast interpretations,
and compare them to structured content, such as a textbook chapter. Finally, learning (or acting) collectively is achieved through
the further synthesis and interpretation of all aspects of the process, in order to
achieve an understanding for application to future situations.1
Researchers have put great effort into
examining the knowledge construction process. In a study focused on problem-based
learning, researchers looked for an association of student questions and knowledge
construction drive.2 Results suggest that student learning is driven
by questions. More specifically, learning is closely related to the ability to
ask the "right" questions. The extent by which the students’
"right" questions could be answered was associated with a continued quest for knowledge – thus stimulating their motivation.2
In an era of recorded lectures and
online student forums, do the same opportunities for asking the
"right" questions, receiving appropriate responses, and sustaining
interest still exist? In this course [Educational Theory and Practice PHMY 545],
we witness firsthand the process of knowledge construction in the setting of an
asynchronous online discussion. We are instructed to first, read and analyze
literature on the topic, such as books and articles. We then read and analyze
our classmates' interpretations of the topic by reviewing the responses posted
on the discussion board. Next, we are encouraged to post our own thoughts on
the topic in response to the instructor's prompts. After reading comments from
our colleagues, both in response to our own posts and to others, we are
encouraged to draw conclusions. Although we may not have realized it, we are
participating in the knowledge construction process! Also, in addition to encouraging high-level thinking, we
are grounded by the instructor's comments. The instructor provides us with answers to
our questions. If we happen to stray away from the purpose of the discussion,
we are re-directed and are led back to asking the "right" questions.
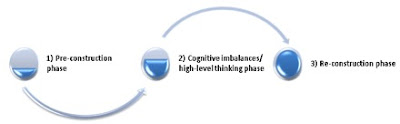
There appears
Applying these concepts to the
discussion board assignment in this course, the pre-construction phase includes gathering the information required
to answer the questions. This includes information from experts (e.g. the thus collaborating with others to build upon our
knowledge.3 The re-construction phase makes us aware of
how our original understand differs from our newly acquired knowledge. This may
include disregarding a previous assumption or going forward with a stronger
understanding and increased confidence in future situations.4
Knowledge construction does not end
when the discussion board is over. In one study, the researchers found that learners
continued to construct their knowledge outside of the online class through
interpretation and application to daily life.4 Our discussion board engenders
application outside the class too. So, in an era of online instruction, do we
have the same opportunities for optimal knowledge construction? The answer is yes! Technology and modern
forms of communication do not hinder us – but they must be used and applied
wisely based an understanding of how learners learn.
References
- Olson, R. Collective Knowledge Construction. Ideas Lab. Available at: http://www.ideaslab.edu/wp-content/uploads/2011/07/Understanding-Virtual-Pedagogies_CKC_ideasLAB. Accessed September 22, 2015.
- Chin C.
and Sci doi sce . - Rahman S, Yasin RM, Jusoff K, et al. Knowledge Construction Process in Online Learning. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 2011; 8: 488-492.
Kanyka